ECE :: Exam Questions Paper
-
The following k-map implements
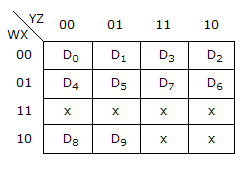
-
The Z-transform of a signal is given by
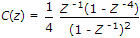 its final value is __________ .
its final value is __________ . -
A surface charge density of 8 nc/m2 is present on a plane x = z. A line charge density of 30 nC/m is present on line x = 1, y = 2 Find VAB for points A(3, 4, 0) and B(4, 0, 1)
-
The electric field vector
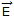 of a wave in free space (εo, μo) is
of a wave in free space (εo, μo) is
Its magnetic field vector will be given by
will be given by -
A uniform plane wave is described by the equation H =
 A/m. If the velocity of the wave is 2 x 108 m/s and εr = 1.8, then. The frequency of the wave is
A/m. If the velocity of the wave is 2 x 108 m/s and εr = 1.8, then. The frequency of the wave is -
Consider two random processes x(t) and y(t) have zero mean, and they are individually stationary. The random process is z(t) = x(t) + y(t). Now when stationary processes are uncorrelated then power spectral density of z(t) is given by



 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook



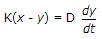
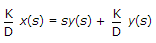
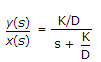
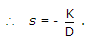
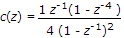
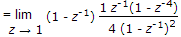
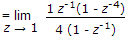
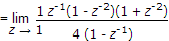
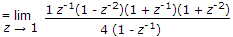

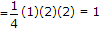 .
.
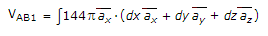
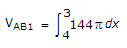
 = 144pv = 452.16v
= 144pv = 452.16v 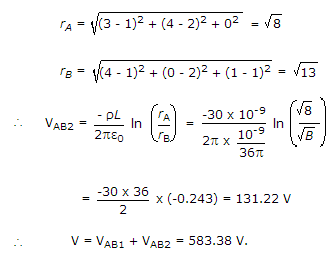

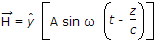
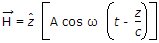
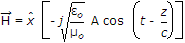


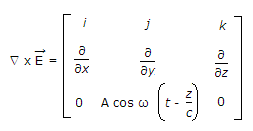


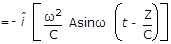 (use B = μ0 H) .
(use B = μ0 H) .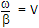
 .
.