Discussion :: Signals and Systems
-
If function f(t) has an initial value f(0-) at t = 0-, the Laplace transform of
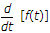 is
is
Answer : Option A
Explanation :
£f(t) = 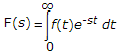
£-1F(s) = f(t)
£[a f1(t) + bf2(t)] = aF1(s) + bF2(s)
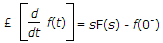
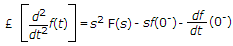
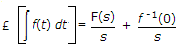
where 
£[f(t - T)] = e-sT F(s)
£[e-at f(t)] = F(s + a)
Initial value theorem 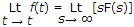
Final value theroem 
Convolution Integral 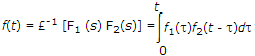
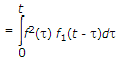
where t is dummy variable for t.
Be The First To Comment


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

