Interview :: MariaDB
MariaDB COUNT() aggregate function is used to return the count of an expression.
The COUNT () Function counts only NOT NULL values.
COUNT (*) counts the total number of rows in a table.
COUNT () would return 0 if there were no matching rows.
Syntax:
Example
We have a table "Students", having the following data:
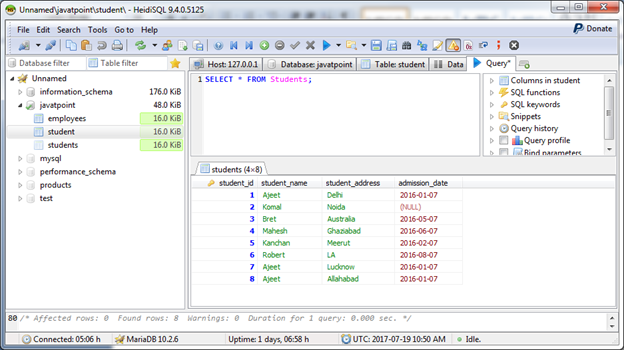
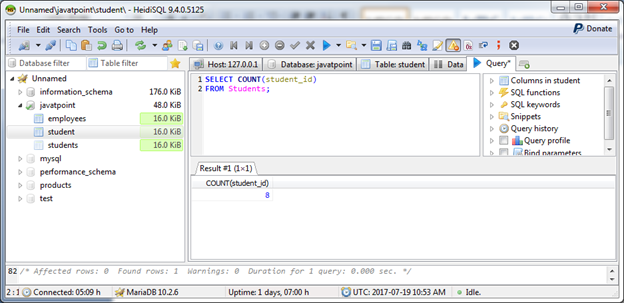
Count "student_id" from "Students" table:
MariaDB SUM function is used to return the summed value of an expression.
If the table has no any rows, then SUM () returns NULL. The DISTINCT keyword is also used with SUM () to sum only the distinct values of an expression.
Syntax:
Example
Table: EMP
| emp_id | emp_salery |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1000 |
| 2 | 2000 |
| 3 | 5000 |
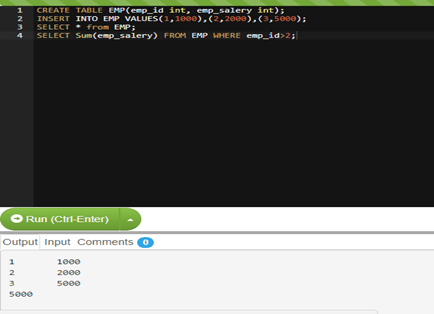
Output:
5000
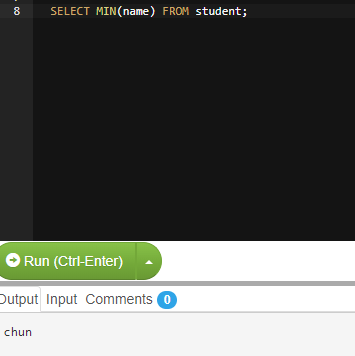
MariaDB MIN() function is used to retrieve the minimum value of the expression.
MIN () can take string argument too, in which case it returns the minimum string values.
MIN() returns NULL if there were no matching rows.
Syntax:
Example
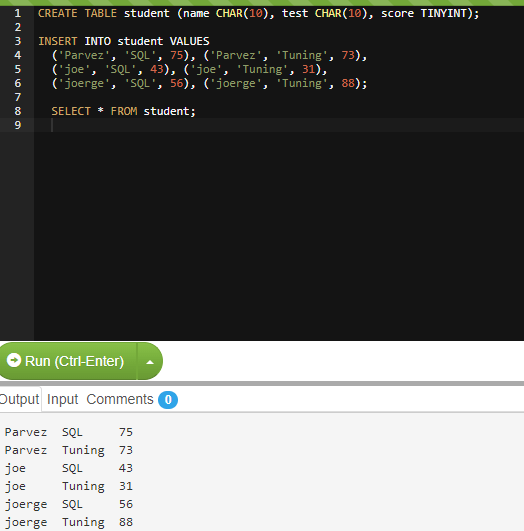
We have a table "Student", having the following data:
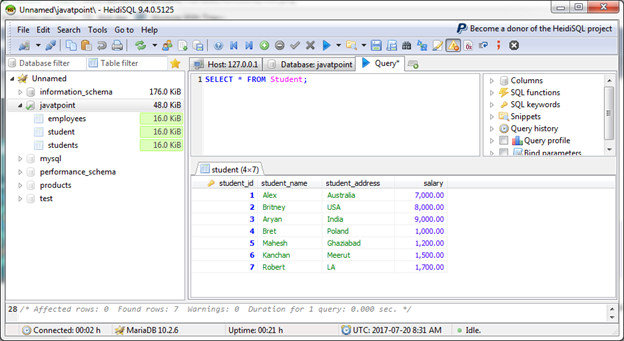
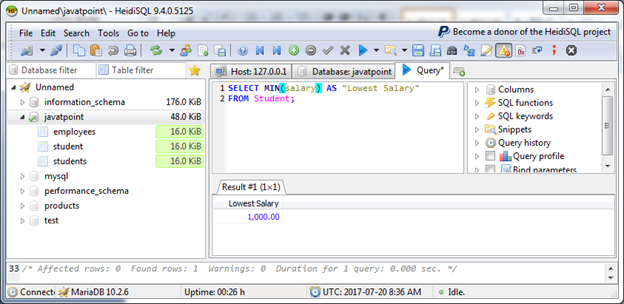
Let's retrieve lowest salary by using MIN () function.
Output:
Let's take another example:
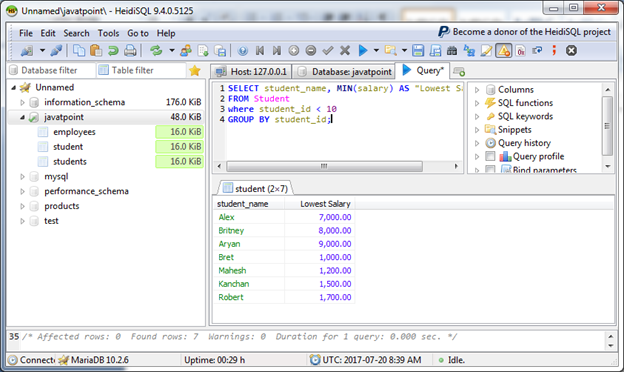
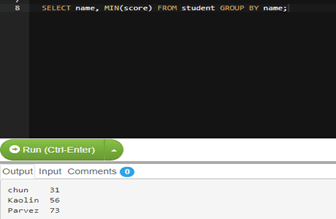
To check MIN string:
MariaDB MAX() function is used to retrieve the maximum value of the expression.
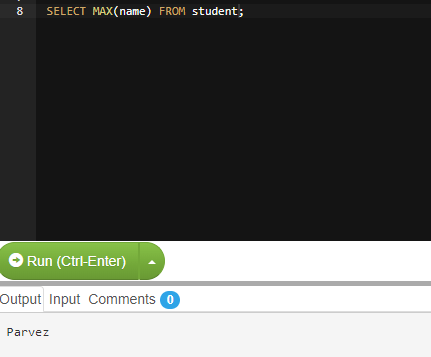
MAX () can take string argument too, in which case it returns the maximum string values.
MAX () returns NULL if there were no matching rows.
Syntax:
Example
We have a "student" table
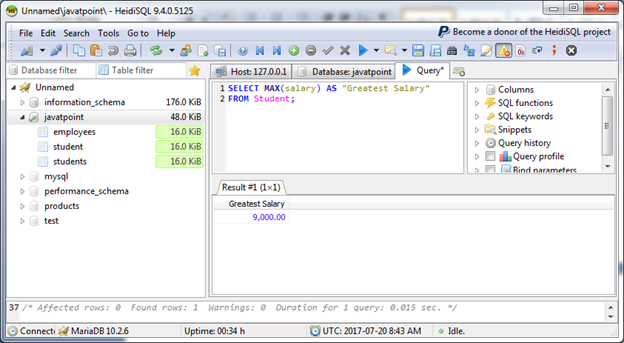
To list out the student name with maximum score:
To check maximum string name:
MariaDB AVG() function is used to retrieve the average value of an expression.
AVG() returns NULL if there were no matching rows.
Syntax:
Or
Example
We have a table "Employee2", having the following data:
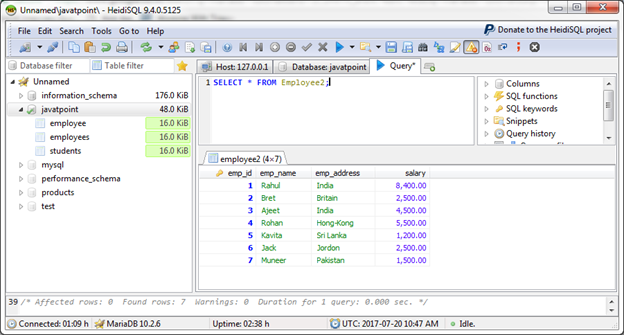
Let's retrieve the average salary of the employees from the table.
Output
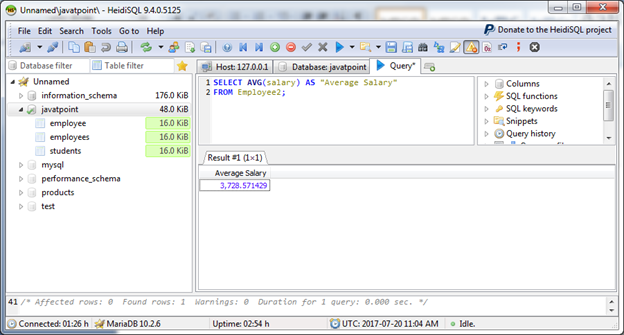
Note: We can Use Average function With formula and ORDER BY clause too.
JOIN is used to retrieve data from two or more tables. By default, JOIN is also called INNER JOIN. It is used with SELECT statement.
There are mainly two types of joins in MariaDB:
INNER JOIN:
MariaDB INNER JOIN is the most common type of join which returns all rows from multiple tables where the join condition is satisfied.
Syntax:
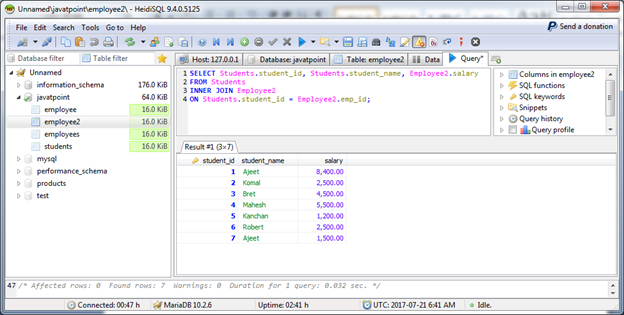
Example
We have two tables "Students" and "Employee2".
Student table
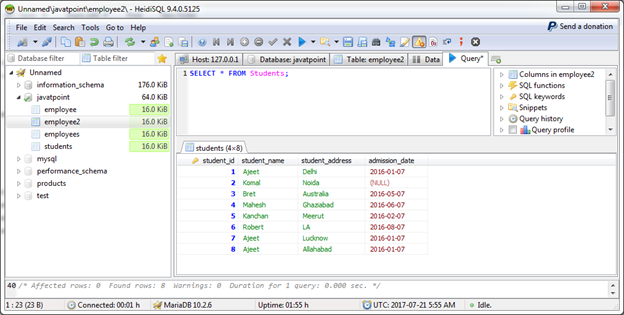
Employee2 Table
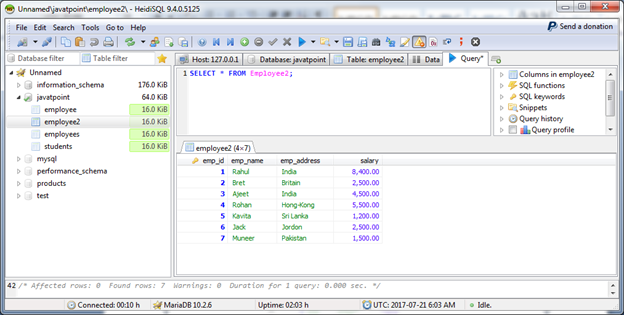
Execute the following commands:
Output
OUTER JOIN:
Again OUTER JOIN is divided into two types:
LEFT JOIN:
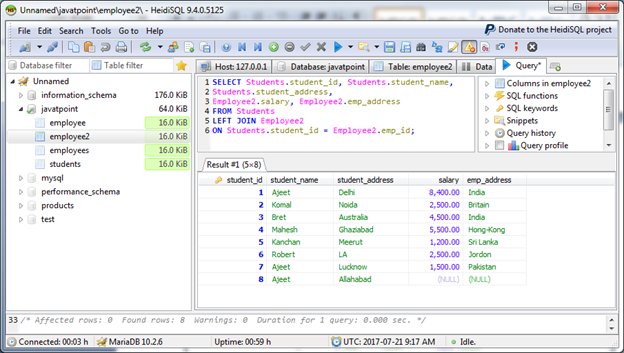
MariaDB LEFT OUTER JOIN is used to return all rows from the left-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined condition is satisfied.
LEFT OUTER JOIN is also called LEFT JOIN.
Syntax:
Example
Output
RIGHT JOIN:
MariaDB RIGHT OUTER JOIN is used to return all rows from the right-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined fields are satisfied with the conditions.
MariaDB RIGHT OUTER JOIN is also called RIGHT JOIN.
Syntax:
Example
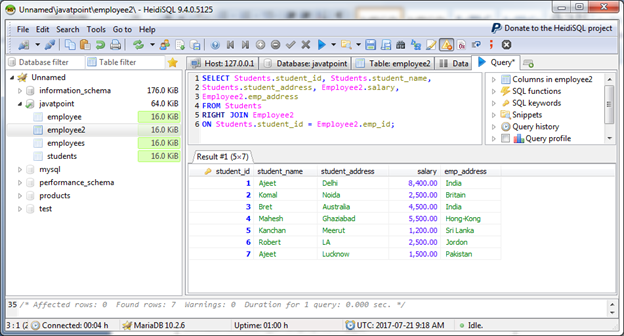
MariaDB INNER JOIN is the most common type of join which returns all rows from multiple tables where the join condition is satisfied.
Syntax:
Example:
What is LEFT OUTER JOIN in MariaDB?
MariaDB LEFT OUTER JOIN is used to return all rows from the left-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined condition is satisfied.
LEFT OUTER JOIN is also called LEFT JOIN.
Syntax:
Example
We have two tables' sites and pages:
Sites table:
| site_id | site_name |
|---|---|
| 100 | Freshergate.com |
| 200 | Facebook.com |
| 300 | Yahoo.com |
| 400 | Google.com |
Pages table:
| page_id | site_id | page_title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | MariaDB |
| 2 | 100 | MySQL |
| 3 | 200 | Java interview questions |
| 4 | 300 | Software testing |
| 5 | 500 | Flight booking |
Now execute the following commands:
Output:
| site_id | site_name | page_id | page_title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | Freshergate | 1 | MariaDB |
| 100 | Freshergate | 2 | MySQL |
| 200 | Facebook.com | 3 | Java interview questions |
| 300 | Yahoo.com | 4 | Software testing |
| 400 | Google.com | null | null |
Site_name Google.com is also included because of LEFT JOIN.
What is RIGHT OUTER JOIN in MariaDB?
MariaDB RIGHT OUTER JOIN is used to return all rows from the right-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined fields are satisfied with the conditions.
MariaDB RIGHT OUTER JOIN is also called RIGHT JOIN.
Syntax:
Example
We have two tables' sites and pages:
Sites table:
| site_id | site_name |
|---|---|
| 100 | Freshergate.com |
| 200 | Facebook.com |
| 300 | Yahoo.com |
| 400 | Google.com |
Pages table:
| page_id | site_id | page_title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | MariaDB |
| 2 | 100 | MySQL |
| 3 | 200 | Java interview questions |
| 4 | 300 | Software testing |
| 5 | 500 | Flight booking |
Now execute the following commands:
Output:
| site_id | site_name | page_id | page_title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | Freshergate | 1 | MariaDB |
| 100 | Freshergate | 2 | MySQL |
| 200 | Facebook.com | 3 | Java interview questions |
| 300 | Yahoo.com | 4 | Software testing |
| null | null | 5 | Flight booking |
Here page_id and page_title contains value because of RIGHT JOIN.
MariaDB function is a stored program that is used to pass parameters into them and return a value
We can easily create and drop functions in MariaDB.
# Create Function (MariaDB):
You can create your own function in MariaDB:
Syntax:
Example
Create a function CalcValue in MariaDB database.
DEFINER clause: it is an optional clause. If not specified, the definer is the user that created the function. If you wish to specify a different definer, you must include the DEFINER clause where user_name is the definer for the function.
function_name: It specifies the name to assign to this function in MariaDB.
return_datatype: It specifies the data type of the function's return value.
LANGUAGE SQL: It is in the syntax for portability but will have no impact on the function.
DETERMINISTIC: It means that the function will always return one result given a set of input parameters.
NOT DETERMINISTIC: It means that the function may return a different result given a set of input parameters. The result may be affected by table data, random numbers or server variables.
CONTAINS SQL: It is the default. It is an informative clause that tells MariaDB that the function contains SQL, but the database does not verify that this is true.
No SQL: An informative clause that is not used and will have no impact on the function.
READS SQL DATA: An informative clause that tells MariaDB that the function will read data using SELECT statements but does not modify any data.
MODIFIES SQL DATA: An informative clause that tells MariaDB that the function will modify SQL data using INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or other DDL statements.
declaration_section: The place in the function where you declare local variables.
executable_section: The place in the function where you enter the code for the function.
Output:
MariaDB DROP Function
You can drop your created function very easily from your database.
Syntax:
Parameter Explanation
function_name: It specifies the name of the function that you want to drop.
Example
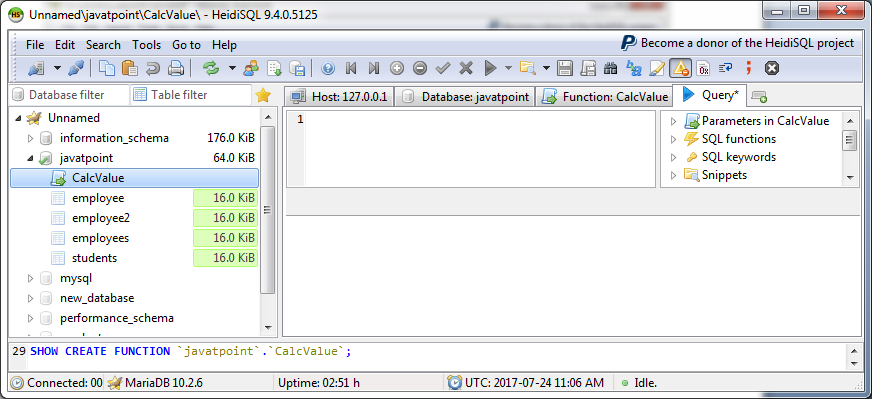
We have created a function name "CalcValue". Now drop the function.
Now you can see that function is deleted and not present in the list anymore.