Civil Engineering :: Theory of Structures
-
By applying the static equations i.e. ΣH = 0, ΣV = 0 and ΣM = 0, to a determinate structure, we may determine
-
The general expression for the B.M. of a beam of length l is the beam carries
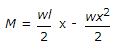
-
The ratio of the length and diameter of a simply supported uniform circular beam which experiences maximum bending stress equal to tensile stress due to same load at its mid span, is
-
If a solid shaft (diameter 20 cm, length 400 cm, N = 0.8 x 105 N/mm2) when subjected to a twisting moment, produces maximum shear stress of 50 N/mm2, the angle of twist in radians, is
-
The maximum B.M. due to an isolated load in a three hinged parabolic arch, (span l, rise h) having one of its hinges at the crown, occurs on either side of the crown at a distance
-
The vertical reaction for the arch is
-
A bar of square section of area a2 is held such that its one of its diameters is vertical. The maximum shear stress will develop at a depth h where h is
-
The equivalent length of a column of length L, having both the ends hinged, is
-
A steel rod of sectional area 250 sq. mm connects two parallel walls 5 m apart. The nuts at the ends were tightened when the rod was heated to 100°C. If αsteel = 0.000012/C°, Esteel = 0.2 MN/mm2, the tensile force developed at a temperature of 50°C, is
-
The ratio of circumferential stress to the longitudinal stress in the walls of a cylindrical shell, due to flowing liquid, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


