GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Metallurgical
- Consider a reaction with activation energy of 8.314 kJ/mol that takes place at 300 K. If the reaction rate is to be tripled, the temperature of the reaction should be
-
Match the processes in Group I with the objectives in Group IIGroup I Group IIP. Vacuum Arc Degassing (VAD) 1. Primary iron makingQ. LD 2. Secondary steel makingR. COREX 3. Direct smeltingS. Blast Furnace 4. Primary steel making
-
The reduction of FeO with CO gas in co-current flow is given by the following equation: FeO + CO = Fe + CO2 ∆Go = 8120 J at 1173 KThe ratio of pCO/pCO2 for this reaction at 1173 K is
-
The sulphide capacity (CS) of liquid slag of composition 55 wt.% CaO, 20 wt.% SiO2, 5 wt.% Al2O3, and 10 wt.% MgO is given by the following equation
log CS = 3.44 (XCaO + 0.1 XMgO - 0.8 XAl2O3 - XSiO2) - (9894/T) + 2.05where, X is mole fraction of the respective components. Atomic weights of Ca, Mg, Si, Al and O are 40, 24, 28, 27 and 16 respectively.The value of CS at 1900 K is -
Identify the correct combination of the following statements P. Bessemer converter can be used in copper smeltingQ. The Mond process for nickel involves reaction of metal with H2 gasR. Roasted ZnS concentrates can be smelted in a blast furnaceS. Magnesium metal can be produced by electrolysis of sea water
-
Match the phases of steel in Group I with the crystal structures in Group IIGroup I Group IIP. Martensite 1. bccQ. Cementite 2. fccR. Austenite 3. bctS. Ferrite 4. Orthorhombic
-
Arrange the following in terms of increasing severity of quench P. Oil quenchingQ. Water quenchingR. Water quenching with agitationS. Brine quenching
- Regarding recrystallization, which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
-
A liquid droplet (β) is on a substrate (δ) and is surrounded by air (α), as shown below. The angle of contact (θ) is determined using the following expression:
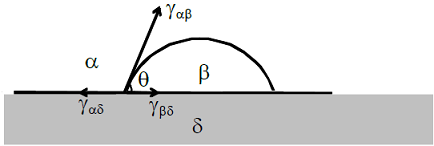
-
Match the phenomena listed in Group I with the possible mechanisms in Group IIGroup I Group IIP. Fatigue 1. Grain boundary slidingQ. Creep 2. Slip band extrusion and intrusionR. Strain hardening 3. Cottrell atmosphereS. Yield point phenomenon 4. Dislocation interaction
|
A.
Higher the amount of cold work, lower is the recrystallization temperature
|
|
B.
Higher the recovery, higher is the recrystallization temperature
|
|
C.
Higher the temperature of cold work, higher is the recrystallization temperature
|
|
D.
Finer the initial grain size, higher is the recrystallization temperature
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


