GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Chemical
- A binary liquid mixture is in equilibrium with its vapor at a temperature T = 300 K. The liquid mole fraction x1 of species 1 is 0.4 and the molar excess Gibbs free energy is 200 J/mol. The value of the universal gas constant is 8.314 J/mol-K, and Ï’i denotes the liquid-phase activity coefficient of species i. If ln(Ï’1) = 0.09, then the value of ln(Ï’2), up to 2 digits after the decimal point, is ________
-
Water (density 1000 kg/m3) is flowing through a nozzle, as shown below and exiting to the atmosphere. The relationship between the diameters of the nozzle at locations 1 and 2 is D1 = 4 D2. The average velocity of the stream at location 2 is 16 m/s and the frictional loss between location 1 and location 2 is 10000 Pa. Assuming steady state and turbulent flow, the gauge pressure in Pa, at location 1 is ___________

- In the elutriation leg of a commercial crystallizer containing a mixture of coarse and very fine crystals of the same material, a liquid is pumped vertically upward. The liquid velocity is adjusted such that it is slightly lower than the terminal velocity of the coarse crystals only. Hence
- 100 ton/h of a rock feed, of which 80% passed through a mesh size of 2.54 mm, were reduced in size such that 80% of the crushed product passed through a mesh size of 1.27 mm. The power consumption was 100 kW. If 100 ton/h of the same material is similarly crushed from a mesh size of 5.08 mm to a mesh size of 2.54 mm, the power consumption (in kW, to the nearest integer) using Bond's law, is _____________
- Calculate the heat required (in kJ, up to 1 digit after the decimal point) to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a solid material from 100oC to 1000oC. The specific heat (CP) of the material (in J/mol-K) is expressed as CP = 20 + 0.005T, where T is in K. Assume no phase change. _________
-
The vapor-liquid equilibrium curve of a binary mixture A-B, may be approximated by a linear equation over a narrow range of liquid mole fractions ( 0.2 < xA < 0.3) as follows y*A = 1.325 xA + 0.121Here y*A is the mole fraction of A in the vapor. 100 moles of a feed (xA, F = 0.28) is batch distilled to a final residue (xA, W = 0.2). Using the Rayleigh equation, the number of moles of the residue left behind in the distillation unit, up to 2 digits after the decimal point, is ____________
- A crosscurrent cascade of N ideal stages is used to treat a feed stream of molar flow rate E. The feed stream contains a solute which is to be recovered by a pure solvent having a molar flow rate S. The solvent is divided equally between these N stages. The linear equilibrium curve relating the mole fractions x and y* of the solute in the raffinate and the extract respectively, is given by y* = m x. Assume dilute conditions. The ratio of the solute mole fraction in the original feed to that in the exit raffinate stream i.e. (x0/xN) is given by
-
A study was conducted in which water was pumped through cylindrical pipes made of a sparingly soluble solid. For a given pipe and certain flow conditions, the mass transfer coefficient kc has been calculated as 1 mm/s using the correlation Sh = 0.025 Re0.6 Sc0.33If the velocity of the fluid and the diameter of the pipe are both doubled, what is the new value of kc in mm/s, up to 2 digits after the decimal point? ____________
-
The gas phase decomposition of azomethane to give ethane and nitrogen takes place according to the following sequence of elementary reactions.
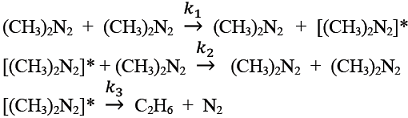 Using the pseudo-steady-state-approximation for [(CH3)2 N2], the order with respect to azomethane in the rate expression for the formation of ethane, in the limit of high concentrations of azomethane, is ___________
Using the pseudo-steady-state-approximation for [(CH3)2 N2], the order with respect to azomethane in the rate expression for the formation of ethane, in the limit of high concentrations of azomethane, is ___________ - A first order liquid phase reaction is carried out isothermally at a steady state in a CSTR and 90% conversion is attained. With the same inlet conditions and for the same overall conversion, if the CSTR is replaced by two smaller and identical isothermal CSTRs in series, the % reduction in total volume, to the nearest integer, is ____________
|
A.
the very fine and coarse crystals will both be carried upward by the liquid
|
|
B.
the very fine and coarse crystals will both settle at the bottom of the tube
|
|
C.
the very fine crystals will be carried upward and the coarse crystals will settle
|
|
D.
the coarse crystals will be carried upward and the very fine crystals will settle
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


